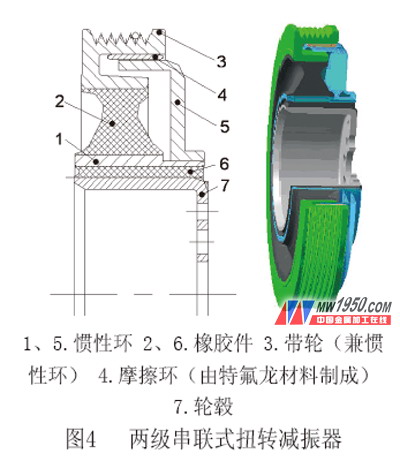
Since the torsional vibration damper composed of the inertia ring 3 and the rubber member 2 is connected in series to the torsional vibration damper composed of the inertia ring and the rubber member 6 synthesized by the inertia rings 5 ​​and 1, the torsion reduction shown in Fig. 4 The vibrator is a two-stage series torsional vibration damper.
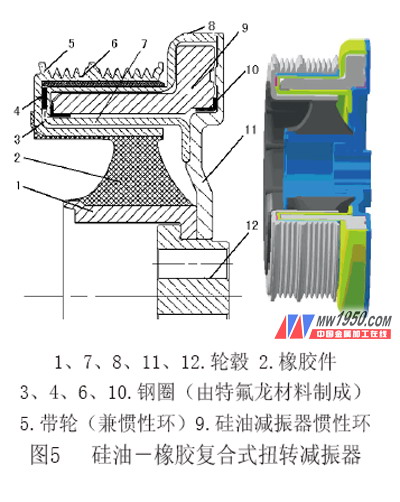
Rubber-silicone oil twist composite damper
Figure 5 shows a silicone oil-rubber two-stage composite crankshaft torsional vibration damper. The hub 12 is coupled to the crankshaft of the engine, and the hubs 1, 11 and the hub 12 are in tight engagement. Both sides of the rubber member 2 are vulcanized together with the hub 1 and the pulley 5, respectively, and the pulley 5 is an inertia ring, which together with the rubber member 2 constitutes a first-stage rubber damping torsional vibration damper. The steel rings 3, 4, 6 and 10 are composed of Teflon materials, and the two objects connected to them can move relative to each other. The inertia ring 9 is an inertia ring of the silicone oil damper, which is filled with silicone oil between the sealing chamber composed of the hubs 11, 7 and 8, and the silicone oil and the inertia ring 9 constitute a first-stage silicone oil damping type torsional vibration damper. Since the rubber damping torsional vibration damper (composed of the elastic damping element and the inertia element) and the silicone oil damping torsional vibration damper are in parallel, the crankshaft damper shown in FIG. 5 is a two-stage parallel silicone oil-rubber. Composite torsional vibration damper.
Previous page next page